Render流程概述
- Trigger
触发渲染 - Render
根据组件返回的 JSX 在内存中依次创建 Fiber节点 并连接在一起构建 Fiber树,被称为 workInProgress Fiber树。 - Commit
workInProgress Fiber 树在 Render 阶段完成构建后进入 commit 阶段渲染到页面上。渲染完毕后,workInProgress Fiber 树变为 current Fiber 树。
Fiber节点是如何被创建并构建Fiber树的
Render
render阶段 开始于 performSyncWorkOnRoot 或 performConcurrentWorkOnRoot 方法的调用。这取决于本次更新是同步更新还是异步更新。
// performSyncWorkOnRoot会调用该方法
function workLoopSync() {
while (workInProgress !== null) {
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
}
// performConcurrentWorkOnRoot会调用该方法
function workLoopConcurrent() {
while (workInProgress !== null && !shouldYield()) {
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);
}
}他们之间的区别是是否调用 shouldYield。如果当前浏览器帧没有剩余时间,shouldYield 会中止循环,直到浏览器有空闲时间后再继续遍历。
workInProgress 代表当前已创建的 workInProgress fiber。
performUnitOfWork 方法会创建下一个Fiber节点并赋值给 workInProgress,并将 workInProgress 与已创建的Fiber节点连接起来构成Fiber树。
// performSyncWorkOnRoot
function performSyncWorkOnRoot(root) {
// ...
let exitStatus = renderRootSync(root, lanes);
// ...
}// performConcurrentWorkOnRoot
function performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(root, didTimeout) {
// ...
let exitStatus = shouldTimeSlice
? renderRootConcurrent(root, lanes)
: renderRootSync(root, lanes);
// ...
}function renderRootConcurrent(root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes) {
// ...
workLoopConcurrent();
// ...
}
function renderRootSync(root: FiberRoot, lanes: Lanes) {
// ...
workLoopSync();
// ...
}Fiber Reconciler 通过遍历方式实现可中断的递归,performUnitOfWork 可以分为两部分:递 和 归
递阶段
从 rootFiber 开始向下深度优先遍历。为遍历到的每个 Fiber节点 调用 beginWork 方法。
该方法会根据传入的 Fiber节点 创建 子Fiber节点,并将这 两个Fiber节点 连接起来。
当遍历到叶子节点(即没有子组件的组件)时就会进入“归”阶段。
归阶段
在“归”阶段会调用 completeWork 处理 Fiber节点 。
当某个 Fiber节点 执行完 completeWork,如果其存在 兄弟Fiber节点(即 fiber.sibling !== null),会进入其 兄弟Fiber 的“递”阶段。
如果不存在 兄弟Fiber,会进入 父级Fiber 的“归”阶段。
“递”和“归”阶段会交错执行直到“归”到 rootFiber 。至此,render 阶段的工作就结束了
作为一种性能优化手段,针对只有单一文本子节点的 Fiber,React 会特殊处理。
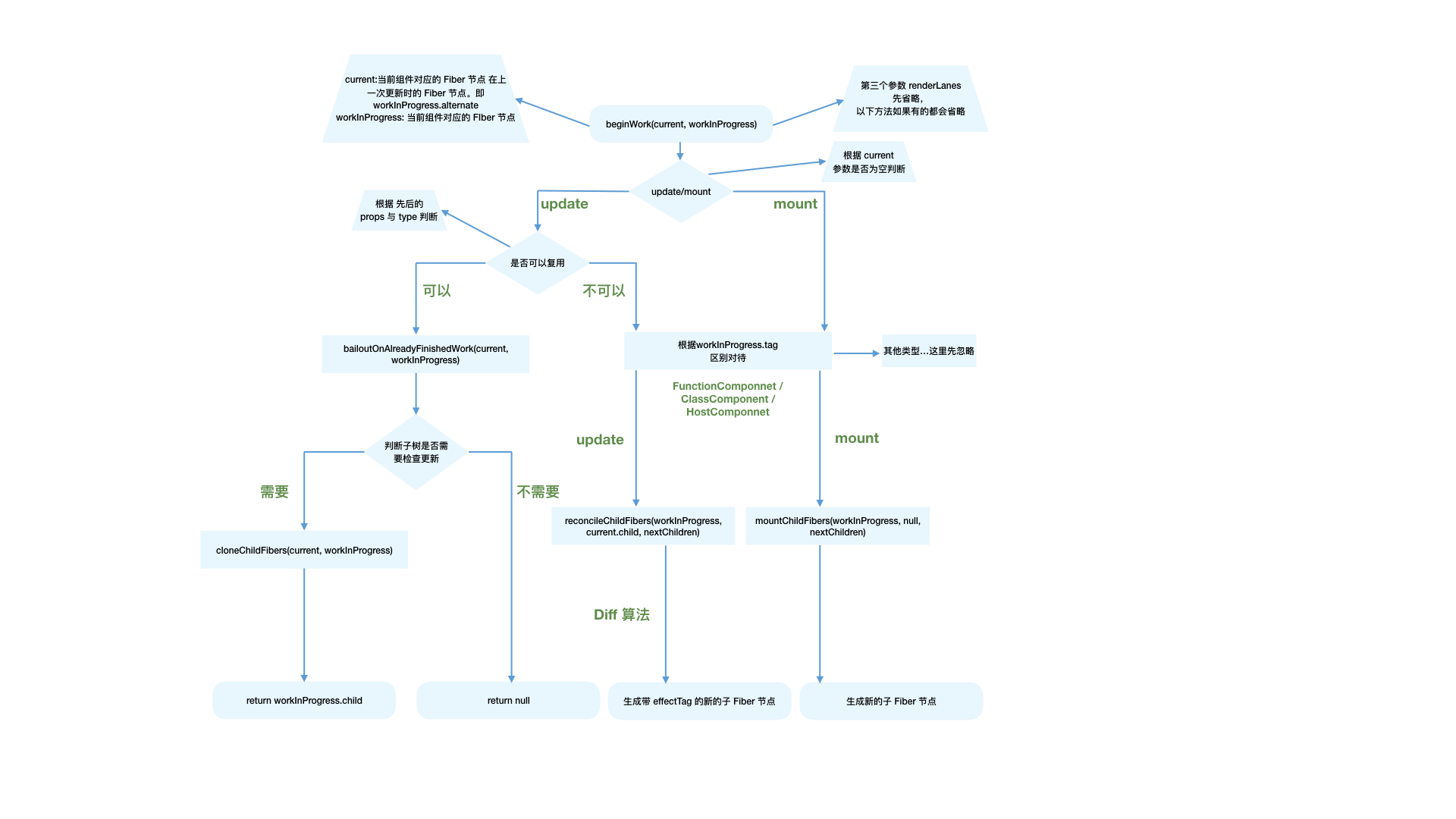
beginWork
beginWork 的工作是传入 当前Fiber节点,创建 子Fiber节点。
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
// ...函数体
}其中传参:
- current 当前组件对应的 Fiber节点 在上一次更新时的 Fiber节点,即 workInProgress.alternate
- workInProgress 当前组件对应的 Fiber节点
- renderLane 优先级相关 Scheduler
组件 mount 时,由于是首次渲染,不存在当前组件对应的Fiber节点在上一次更新时的Fiber节点。此时current === null,因此通过 current === null ? 来区分组件是处于 mount 还是 update
beginWork 的工作可以分为两部分:
update:如果 current 存在,在满足一定条件时可以复用 current节点,这样就能克隆 current.child 作为 workInProgress.child,而不需要新建 workInProgress.child。
mount:除 fiberRootNode 以外,current === null。会根据 fiber.tag 不同,创建不同类型的 子Fiber节点
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes
): Fiber | null {
// update时:如果current存在可能存在优化路径,可以复用current(即上一次更新的Fiber节点)
if (current !== null) {
// ...省略
// 复用current
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(
current,
workInProgress,
renderLanes,
);
} else {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
}
// mount时:根据tag不同,创建不同的子Fiber节点
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
// ...省略
case LazyComponent:
// ...省略
case FunctionComponent:
// ...省略
case ClassComponent:
// ...省略
case HostRoot:
// ...省略
case HostComponent:
// ...省略
case HostText:
// ...省略
// ...省略其他类型
}
}update时
满足如下情况时 didReceiveUpdate === false(即可以直接复用前一次更新的子Fiber,不需要新建子Fiber)
- oldProps === newProps && workInProgress.type === current.type,即 props 与 fiber.type 不变
- !includesSomeLane(renderLanes, updateLanes),即当前 Fiber节点 优先级不够
if (current !== null) {
const oldProps = current.memoizedProps;
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
if (
oldProps !== newProps ||
hasLegacyContextChanged() ||
(__DEV__ ? workInProgress.type !== current.type : false)
) {
didReceiveUpdate = true;
} else if (!includesSomeLane(renderLanes, updateLanes)) {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
// 省略处理
}
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(
current,
workInProgress,
renderLanes,
);
} else {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
}
} else {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
}mount时
当不满足优化路径时,进入第二部分,新建 子Fiber。
根据 fiber.tag 不同,进入不同类型 Fiber 的创建逻辑。
// mount时:根据tag不同,创建不同的Fiber节点
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
// ...省略
case LazyComponent:
// ...省略
case FunctionComponent:
// ...省略
case ClassComponent:
// ...省略
case HostRoot:
// ...省略
case HostComponent:
// ...省略
case HostText:
// ...省略
// ...省略其他类型
}对于常见的组件类型,如(FunctionComponent/ClassComponent/HostComponent),最终会进入 reconcileChildren方法。
reconcileChildren
对于 mount 的组件,他会创建新的 子Fiber节点
对于 update 的组件,他会将当前组件与该组件在上次更新时对应的 Fiber节点 比较(Diff算法 ),将比较的结果生成 新Fiber节点
export function reconcileChildren(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
nextChildren: any,
renderLanes: Lanes
) {
if (current === null) {
// 对于mount的组件
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(
workInProgress,
null,
nextChildren,
renderLanes,
);
} else {
// 对于update的组件
workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(
workInProgress,
current.child,
nextChildren,
renderLanes,
);
}
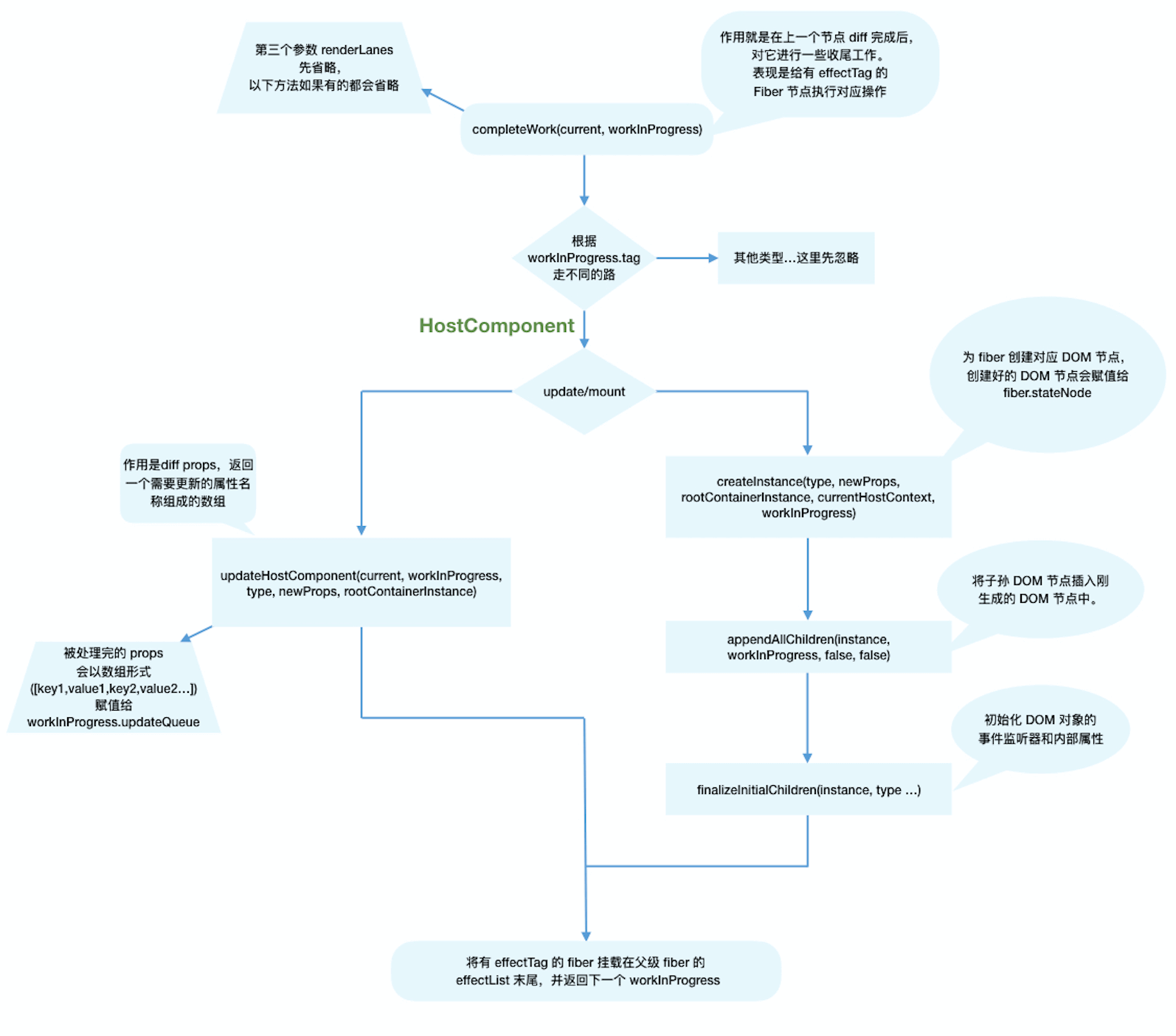
}completeWork
流程概述
类似 beginWork ,completeWork 也是针对不同 fiber.tag 调用不同的处理逻辑。
function completeWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): Fiber | null {
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
case LazyComponent:
case SimpleMemoComponent:
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case Fragment:
case Mode:
case Profiler:
case ContextConsumer:
case MemoComponent:
return null;
case ClassComponent: {
// ...省略
return null;
}
case HostRoot: {
// ...省略
updateHostContainer(workInProgress);
return null;
}
case HostComponent: {
// ...省略
return null;
}
// ...省略处理 HostComponent
HostComponent 即原生 DOM组件 对应的 Fiber节点
和 beginWork 一样,根据 current === null ? 判断是 mount 还是 update。
同时针对 HostComponent,判断 update 时还需要考虑 workInProgress.stateNode != null ?(即该 Fiber节点 是否存在对应的 DOM节点 )
case HostComponent: {
popHostContext(workInProgress);
const type = workInProgress.type;
if (current !== null && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {
// update的情况
// ...省略
} else {
// mount的情况
// ...省略
}
return null;
}update
当 update 时,Fiber节点 已经存在对应 DOM节点,所以不需要生成 DOM节点。需要做的主要是处理 props
例如:
- onClick、onChange 等回调函数的注册
- 处理 style prop
- 处理 DANGEROUSLY_SET_INNER_HTML prop
- 处理 children prop
if (current !== null && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {
// update 情况
updateHostComponent(current, workInProgress, type, newProps);
}在 updateHostComponent 内部,被处理完的 props会被赋值给 workInProgress.updateQueue,并最终会在 commit阶段 被渲染在页面上
workInProgress.updateQueue = (updatePayload: any);其中 updatePayload 为数组形式,他的偶数索引的值为变化的 prop key,奇数索引的值为变化的 prop value
mount
mount时的主要逻辑包括三个
- 为 Fiber节点 生成对应的 DOM节点
- 将 子孙DOM节点 插入刚生成的 DOM节点 中
- 与 update 逻辑中的 updateHostComponent 类似的处理 props 的过程
// mount的情况
// ...省略服务端渲染相关逻辑
const currentHostContext = getHostContext();
// 为fiber创建对应DOM节点
const instance = createInstance(
type,
newProps,
rootContainerInstance,
currentHostContext,
workInProgress,
);
// 将子孙DOM节点插入刚生成的DOM节点中
appendAllChildren(instance, workInProgress, false, false);
// DOM节点赋值给fiber.stateNode
workInProgress.stateNode = instance;
// 与update逻辑中的updateHostComponent类似的处理props的过程
if (
finalizeInitialChildren(
instance,
type,
newProps,
currentHostContext,
)
) {
markUpdate(workInProgress);
}mount 时只会在 rootFiber 存在 Placement effectTag。
commit阶段 是如何通过一次插入DOM操作(对应一个 Placement effectTag )将 整棵DOM树 插入页面的呢?
原因就在于 completeWork 中的 appendAllChildren 方法。
由于 completeWork 属于“归”阶段调用的函数,每次调用 appendAllChildren 时都会将已生成的 子孙DOM节点 插入当前生成的DOM节点下。那么当“归”到 rootFiber 时,我们已经有一个构建好的离屏DOM树
effectList
至此 render 阶段的绝大部分工作就完成了。
在 completeWork 的上层函数 completeUnitOfWork 中,每个执行完 completeWork 且存在 effectTag 的 Fiber节点 会被保存在一条被称为effectList的单向链表中。
effectList 中第一个 Fiber节点 保存在 fiber.firstEffect,最后一个元素保存在 fiber.lastEffect。
类似 appendAllChildren,在“归”阶段,所有有 effectTag 的 Fiber节点 都会被追加在 effectList 中,最终形成一条以 rootFiber.firstEffect 为起点的单向链表。
nextEffect nextEffect
rootFiber.firstEffect -----------> fiber -----------> fiber在 commit阶段 只需要遍历 effectList 就能执行所有 effect 了
至此,render阶段 全部工作完成。在 performSyncWorkOnRoot 函数中 fiberRootNode 被传递给 commitRoot 方法,开启 commit阶段 工作流程。
commitRoot(root);参考图片
beginWork 流程图
completeWork 流程图